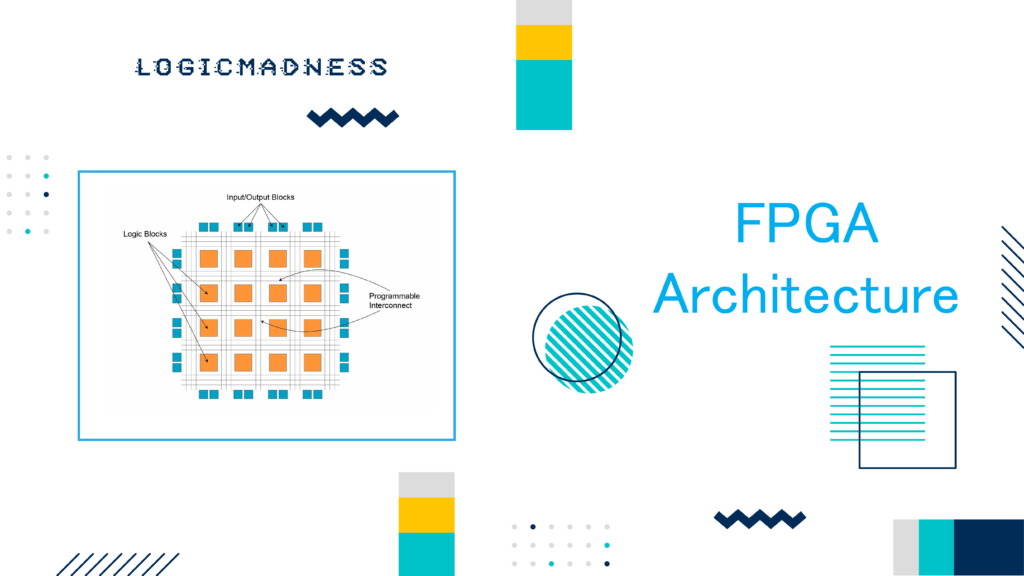
Data centers are growing rapidly as the demand for cloud services, big data, and artificial intelligence continues to rise. Managing power efficiently has become one of the most important challenges for data center operators. Poor power management can lead to higher operational costs, larger carbon footprints, and worse performance. To overcome these challenges, more organizations are turning to innovative technologies that provide real-time insights and automated control over power usage. One such technology is the Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). This article explains how FPGAs can improve power management in data centers and help operators reduce costs and increase energy efficiency.
What Are FPGAs and How Do They Help in Power Management?
FPGAs are specialized hardware that can be programmed to perform specific tasks efficiently. Unlike traditional processors, FPGAs can be customized to handle complex tasks such as real-time data processing and monitoring. In data centers, FPGAs provide several advantages when it comes to managing power consumption:
- Parallel Processing: FPGAs can process multiple tasks at the same time, making them faster than traditional CPUs.
- Low Latency: They can analyze power data quickly and respond in real time.
- Reconfigurability: FPGAs can be reprogrammed, which makes them adaptable to changing power management needs.
These features make FPGAs ideal for real-time power management in data centers. Let’s take a closer look at how FPGAs are used for this purpose.
Key Roles of FPGAs in Real-Time Power Management
FPGAs can help optimize power usage in data centers in several ways. Here are the most important roles they play:
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Acquisition
- Sensors and Data Inputs: FPGAs can connect to various sensors to track power usage, temperature, and voltage. They can monitor each component of the data center to provide a detailed overview of energy consumption.
- Fast Data Processing: Thanks to their parallel processing ability, FPGAs can analyze large amounts of data quickly, ensuring operators get timely updates about power consumption and system performance.
2. Implementing Dynamic Power Scaling
- Adaptive Power Distribution: FPGAs can adjust the power supply based on real-time usage. For example, they can increase power to areas of high demand and reduce power to underused components.
- Load Shifting: When power demand exceeds supply, FPGAs can temporarily reduce power to non-essential systems, ensuring that critical operations continue without interruption.
3. Seamless Integration with Existing Infrastructure
- Communication Protocols: FPGAs work with existing power management systems using standard communication protocols like I2C, SPI, and CAN, making it easy to integrate with power distribution units (PDUs) and other equipment.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): FPGAs can interface directly with PDUs to monitor and control power usage at a granular level. This ensures that each rack or server gets the correct amount of power based on current needs.
4. Fault Detection and Reliability
- Real-Time Anomaly Detection: FPGAs can monitor power data to identify unusual spikes or temperature changes, which could indicate potential problems.
- Enhanced Fault Tolerance: FPGAs are reconfigurable, meaning they can quickly reroute power or adjust settings if there’s a system failure, maintaining continuous operations.
Benefits of Using FPGAs for Power Management
FPGAs offer a range of benefits that make them an excellent choice for managing power in data centers. Let’s look at the key advantages:
1. Increased Efficiency and Performance
- Real-Time Processing: FPGAs process power data instantly, ensuring optimal resource allocation and reducing energy waste.
- Parallel Processing: FPGAs can handle multiple tasks at once, enabling quicker decision-making and improving overall system performance.
2. Cost Savings Through Energy Optimization
- Reduced Energy Consumption: FPGAs enable efficient power distribution, cutting down on electricity usage and lowering costs for large data centers.
- Lower Operational Costs: By preventing over-provisioning of power, FPGAs reduce the need for additional hardware upgrades, cooling systems, and maintenance.
3. Improved Reliability and Fault Tolerance
- Predictive Maintenance: Continuous monitoring by FPGAs allows for early detection of potential issues, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Redundant Systems: FPGAs can implement failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted service, even in case of a component failure.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
- Easy Upgrades: FPGAs can be reprogrammed as technology evolves, allowing data centers to adjust their power management strategies without major hardware changes.
- Custom Solutions: Data centers can develop tailored power management solutions using FPGAs, which is especially useful for complex or unique requirements.
5. Better Monitoring and Control
- Granular Monitoring: FPGAs allow for detailed tracking of power consumption at the component level, ensuring precise adjustments.
- IoT Integration: FPGAs can connect with Internet of Things (IoT) devices to further enhance monitoring and control of power systems.
6. Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By optimizing energy usage, FPGAs help lower carbon emissions, contributing to sustainability goals.
- Renewable Energy Integration: FPGAs facilitate the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, in data centers, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Future Trends in FPGA Power Management
As data centers continue to evolve, FPGA technology will play a more prominent role in power management. Here are some key trends to watch for in the coming years:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
- Smarter Power Management: AI-powered systems will work with FPGAs to predict power usage patterns and automatically adjust power distribution.
- Better Anomaly Detection: Machine learning will improve the ability of FPGAs to detect and respond to potential issues before they cause downtime.
2. Edge Computing
- Local Power Management: As edge computing grows, FPGAs will be essential for managing power in localized systems where real-time processing is crucial.
3. IoT Expansion
- Interconnected Ecosystems: The growing number of IoT devices will require FPGAs to manage power across all devices in a network, optimizing energy usage across a whole facility.
4. Customization and Flexibility
- Dynamic Reconfiguration: FPGAs will become even more adaptable, allowing data centers to adjust power management strategies as needed.
- User-Friendly Development Tools: Advances in FPGA programming tools will make it easier for operators to implement customized power management solutions.
5. Sustainability and Green Computing
- Renewable Energy Integration: FPGAs will continue to support the use of renewable energy in data centers, helping companies meet sustainability targets.
- Carbon Footprint Monitoring: Future FPGA systems will include features to track and report carbon footprints, helping data centers reduce emissions.
6. Advances in FPGA Technology
- Improved Efficiency: Ongoing advancements in FPGA technology will lead to faster, more efficient chips that consume less power.
- Smaller and More Powerful FPGAs: The trend toward miniaturization will result in smaller FPGAs with more processing power, making them suitable for a wider range of applications.
Conclusion: Why FPGAs Are Essential for Real-Time Power Management in Data Centers
FPGAs are transforming power management in data centers. Their ability to monitor power usage in real time, scale power distribution dynamically, and detect faults makes them an invaluable tool for improving energy efficiency and reducing costs. As technology advances, FPGAs will play an even larger role in integrating renewable energy, enhancing system reliability, and supporting sustainability goals. For data center operators looking to optimize power management, adopting FPGA technology is an essential step toward improving efficiency and driving long-term success.